What is an Optical fiber & its Construction [Basics]
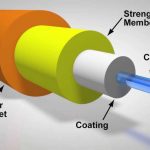
What is an optical fiber? what is an optical fiber ? Typically, fiber optics are long, thin strands of glass (SiO2) about the diameter of human hair; some can be made out of plastic. Long distance telecommunication systems always use glass because of its lower optical absorption during transmission to maintain the signal strength. When …
Continue reading ‘What is an Optical fiber & its Construction [Basics]’ »